According to an analysis, Qatar spent USD 220 billion on the World Cup. The country will have to sell about three billion barrels of crude oil to cover the tournament’s cost, according to TradingPedia. Its use will cause 928 million metric tons of CO2 emissions into the atmosphere.
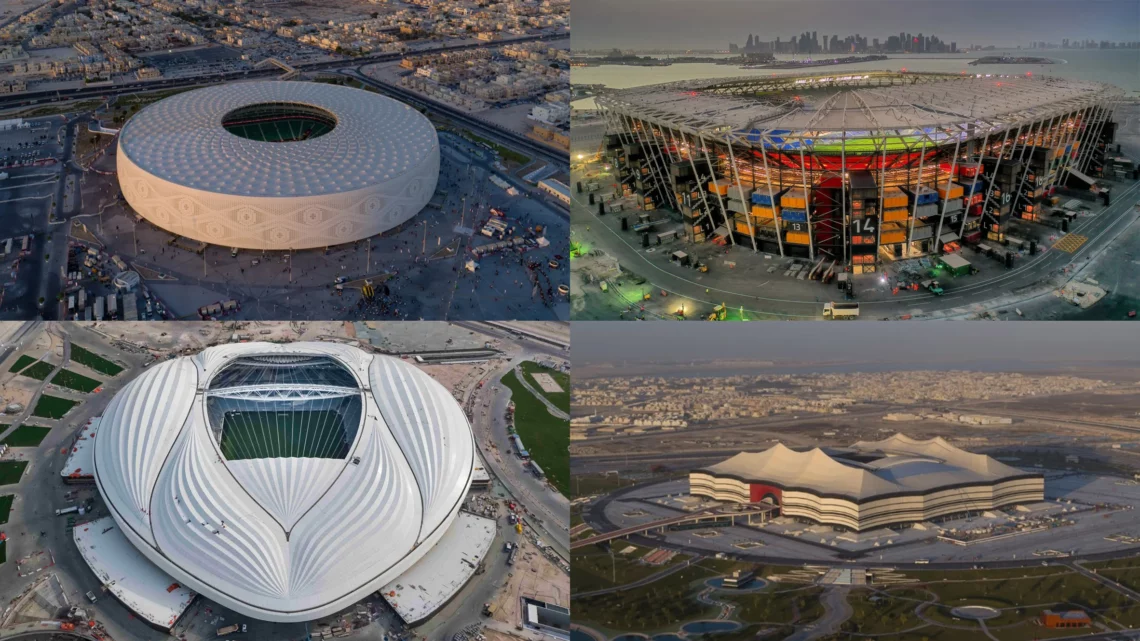
The total cost of preparing and organizing the 2022 FIFA World Cup is estimated at USD 220 billion. Over the past 12 years, preparations for the football tournament have included the construction of seven stadiums, renovation of one other, and building roads, hotels, metro systems, and other infrastructure for 1.5 million expected visitors.
The cost of preparing and organising the 2022 FIFA World Cup is estimated at USD 220 billion
The combustion of three billion barrels of crude oil results in emissions of 928 million metric tons of carbon dioxide. That much oil is needed to pay off Qatar’s overall World Cup investment, according to an analysis published by TradingPedia, based on the average spot price of Dukhan crude oil from 2010 to 2021 of USD 75.16 per barrel.
The news website said, “Wider investments” that the country has made over the past decade to host the football tournament were also taken into account.
It is by far the most expensive World Cup of all time. By comparison, the 2018 World Cup in Russia cost USD 11.6 billion; the 2014 tournament in Brazil cost USD 15 billion, and the 2010 event in South Africa was valued at USD 3.6 billion.
Qatar’s oil export revenue amounted to EUR 32.28 billion in 2021.
Like most other Persian Gulf states, Qatar supplies vast amounts of oil and natural gas abroad, which accounts for the bulk of its revenue. The country is the world’s largest liquefied natural gas (LNG) exporter.
According to data from Qatar’s budget cited by TradingPedia, oil revenue amounted to EUR 32.28 billion in 2021. Last year’s daily production was estimated at 1.82 million barrels or 2 per cent of global supply.
According to the analysis, it will take Qatar more than four years to fully pay off the tournament costs if the production continues at this rate.
The country has around 25.24 billion barrels in oil reserves, which are projected to last for another 38 years. It will have to pump out and export 11.88 per cent of the total to cover the World Cup investment.
The carbon footprint of the investment.
In 2021, 36.3 billion metric tons of CO2 were emitted from the combustion of fossil fuels in the world. Thus, the carbon footprint of the 2022 World Cup is equivalent to nine days of the global tally, the report adds.
With the average gasoline car emitting approximately 4.6 metric tons of CO2 per year, the analysis reveals the repayment of the Qatar World Cup is equivalent to the annual emissions of 201 million cars.
Questionable climate action
FIFA estimated that the current tournament would cause 3.6 million tons in CO2 emissions or 1.5 million tons more than the 2018 World Cup. It is more than some countries’ annual carbon footprint.
The organisers undertook to use climate-neutral technologies for constructing eight stadiums. They used more than 90 per cent of recycled materials for the endeavor. Qatar has promised to reduce unnecessary energy costs during matches and to provide zero-emission public transport for fans.
In a report, Carbon Market Watch (CMW) questioned the zero emissions of new stadiums, as their use after the World Cup was not precisely determined.
Culled from https://balkangreenenergynews.com