Most Nigerians do not keep track of Information about their livestock and they find it difficult to trace vital information when the need arises. In modern day, livestock identification and traceability have become widely recognized as essential for ensuring the safety of livestock products and facilitating veterinary disease surveillance and control. Electronic identification (E-ID) by using radio frequency identification (RFID), passive transponders, improves traceability due to faster monitoring of livestock and easier management of databases for monitoring,inventory and movement between premises.
Introduction
Traceability refers to “the ability to trace (identify and measure) and follow a food, feed, food producing animal or ingredients, through all stages of production and distribution”. A traceability system is considered as an indispensable instrument to improve consumer confidence in animal produce and food consumption to reduce the asymmetry of information across its supply chains. Traceability systems have been implemented in many countries and regions. Traceability systems in Animal science enhance livestock production and trade by enabling improved surveillance and management of infectious diseases, control of livestock movement, inventory records and effective depiction of production information systems through zoning and breaking down of processes due access to information along productive market chains.
Importance of Traceability of Livestocks
According to studies, traceability, for livestock, poultry and meat can be used;
- to determine origin and ownership, and to deter theft and misrepresentation, of animals and meat;
- for surveillance, control and eradication of exotic animal diseases;
- for biosecurity protection of the national livestock population;
- for compliance with the requirements of international customers(if any);
- for improvement of supply-side management, distribution/delivery systems and inventory controls;
- to isolate the source and extent of quality-control and food-safety problems; and
- to minimize product recalls and make crisis management protocols more effective.
RFID-based traceability system that incorporates RFID tags and readers which can perform traceability throughout an animal’s life cycle and provide accurate traceability information.
Livestock Identification in Nigeria
In modern day agriculture, livestock are bred using the intensive system, in which the animals are kept in an enclosed space, fed by human-provided food and are bred in a controlled environment. However, some livestock are raised using the nomadic system in which they are allowed to roam freely and source their feed from nature .
Historically, livestock raising was part of a nomadic or pastoral form of material culture. The herding of camels and cattle in some parts of Nigeria remains unassociated with sedentary agriculture. The transhumance form of herding in certain parts of Nigeria still continues, as cattle, sheep or goats are moved from one region to the other.
Livestock may be branded to indicate ownership and age but in modern farming, identification is more likely to be done by means of ear tags and electronic identification and this can be achieved with RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology.
The use of RFID in the agricultural sector spans across two major areas, which are quality and safety. Customers are more concerned with receiving information about the food they purchase and consume, they also want to know more about the raw materials used in food production, the origin of materials used in the production, the process history and handling action during delivery.
What is Radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology ?
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) is the wireless use of electromagnetic fields to transfer information for the purpose of automatically identifying and tracking tags attached to objects. These objects can be animals, books and so on. There are specified types of tags which can be attached to the objects. In the context of animal traceability, ear tags are popularly used. The ear tags contain electronically stored information which are powered by electromagnetic induction from magnetic fields produced near the reader.
How does RFID technology work ?
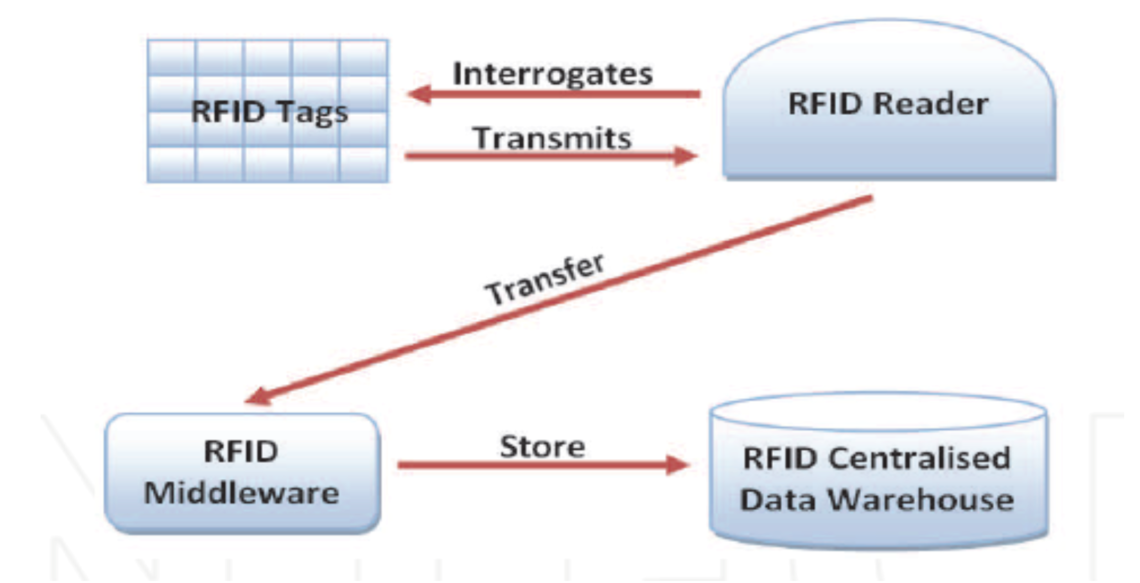
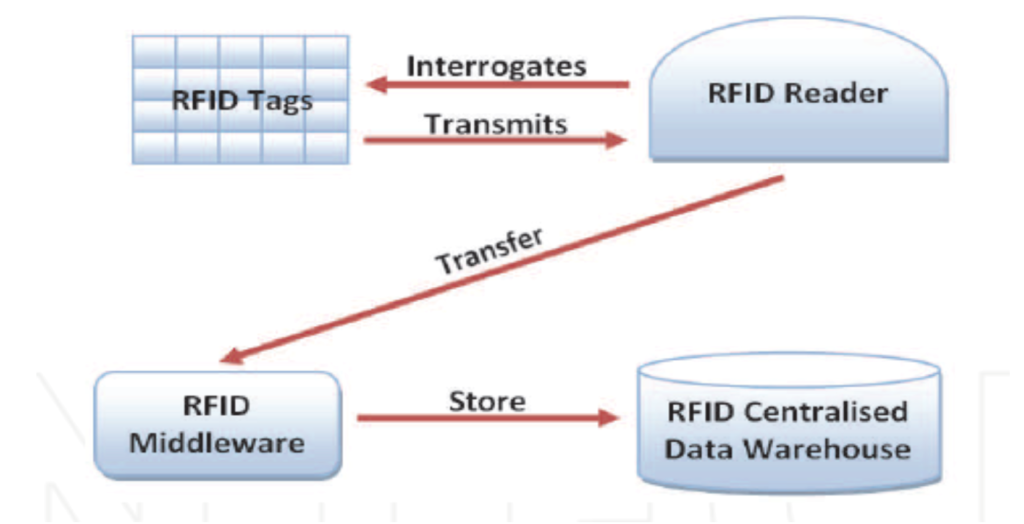
The System Architecture of an RFID system contains four important components; an RFID Tag, an RFID Reader, the RFID Middleware and the Database Storage.
The RFID Tag is the simplest, lowest level component of the RFID System Architecture. The Tag itself is made up of three different components namely ;the Chip which holds the information the tag is to dispense, the Antenna used to transmit the signal out and the Packaging which houses the Chip and Antenna. The Packaging may be applied to the surface of other items.
A Tag RFID is attached to a livestock from birth.. This tag contains all necessary information about the animal. Information in the tag could include the Name , date of birth , treatment schedule amongst many others . This information can be updated at any time and can also be retrieved via a RFID reader at any point in time when needed. An attachable RFID tag or transponder can also be used for animal identification. These tags are powered by electromagnetic induction from magnetic fields produced near the reader. Some tags collect energy from the interrogating radio waves and act as a passive transponder. Other types have a local power source such as a battery and may operate at hundreds of meters from the reader. Unlike a barcode, the tag does not necessarily need to be within line of sight of the reader (where the barcodes on the object would have to be scanned by the barcode readers) and may be embedded in the tracked object. RFID is one method for Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC).
Conclusion
Nigeria as a country can benefit from this technology by implementing it in animal identification management . Basically, developing an RFID-based traceability system in animal science would improve production, data capture and management of livestocks in Nigeria
 Email: Olufemititilayosamuel@gmail.com
Email: Olufemititilayosamuel@gmail.com
Samuel, a Software Engineer